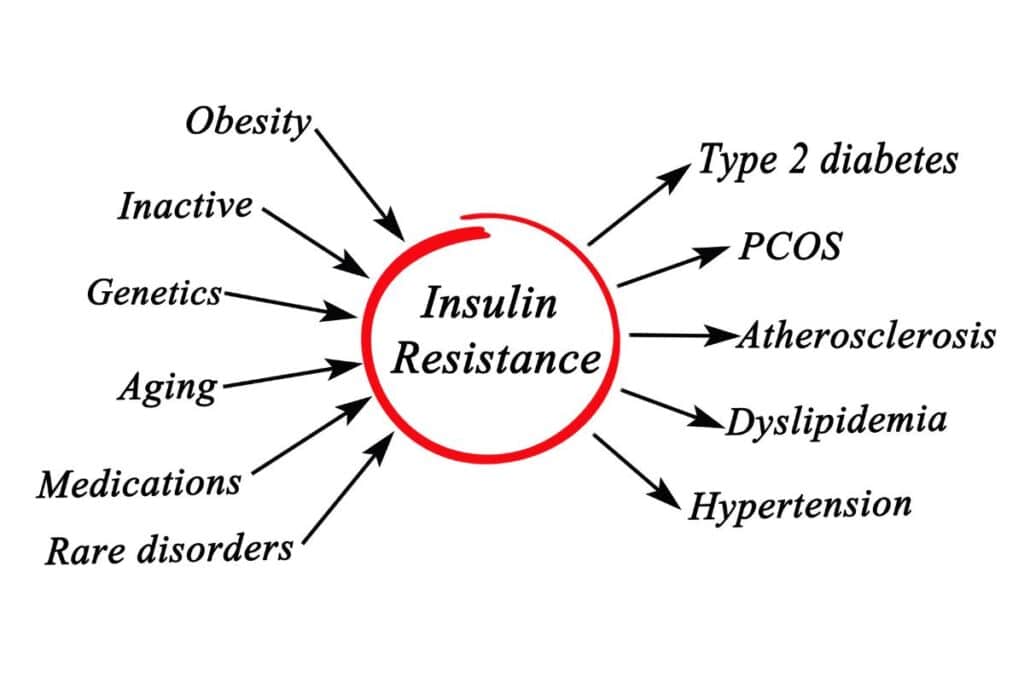
Insulin resistance has emerged as a significant health challenge, closely associated with conditions such as metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. However, adopting the right dietary strategies can effectively manage and even reverse insulin resistance. This article explores the most beneficial diet for insulin resistance and provides additional tips to enhance metabolic health.
Understanding Insulin Resistance:
Before delving into dietary specifics, it’s crucial to understand what insulin resistance entails. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates glucose uptake from the bloodstream into cells. Insulin resistance occurs when cells in muscles, fat, and the liver start resisting or ignoring the signal that the hormone insulin is trying to send out— which is to grab glucose out of the bloodstream and put it into our cells. Glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the body’s main source of energy.
The Best Diet for Insulin Resistance:
Several dietary patterns can help improve insulin sensitivity, but the common thread involves high fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and low glycemic index (GI) foods.
1. Whole Foods Over Processed Foods:
– Embrace whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables.
– Minimize intake of highly processed carbohydrates, which can spike blood sugar levels.
2. High-Fiber Foods:
– Aim for a fiber-rich diet that includes vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains.
– Fiber slows down digestion, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar.
3. Healthy Fats:
– Incorporate sources of omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
– Choose monounsaturated fats from avocados, olive oil, and almonds.
4. Lean Proteins:
– Include lean protein sources such as chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, and legumes.
– Protein has minimal impact on blood glucose levels and can promote satiety.
5. Low Glycemic Index Foods:
– Select foods with a low glycemic index that cause a slower rise in blood sugar.
– Berries, non-starchy vegetables, and sweet potatoes are excellent choices.
Additional Dietary Tips:
1. Mindful Eating:
– Pay attention to hunger cues and avoid overeating.
– Practice mindful eating to promote better digestion and control portion sizes.
2. Regular Meals:
– Eat at regular intervals to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
– Avoid long periods of fasting or skipping meals, which can lead to overeating.
3. Hydration:
– Drink plenty of water to maintain hydration and help regulate blood sugar.
4. Limit Sugary Beverages:
– Reduce intake of sodas, fruit juices, and energy drinks that are high in sugar and can lead to blood sugar spikes.
Conclusion:
Adopting a diet for insulin resistance involves a holistic approach to food, focusing on nutrient-dense, minimally processed ingredients that support stable blood sugar levels. Combined with regular physical activity and lifestyle adjustments, these dietary changes can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and overall health.
Remember, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have underlying health conditions.