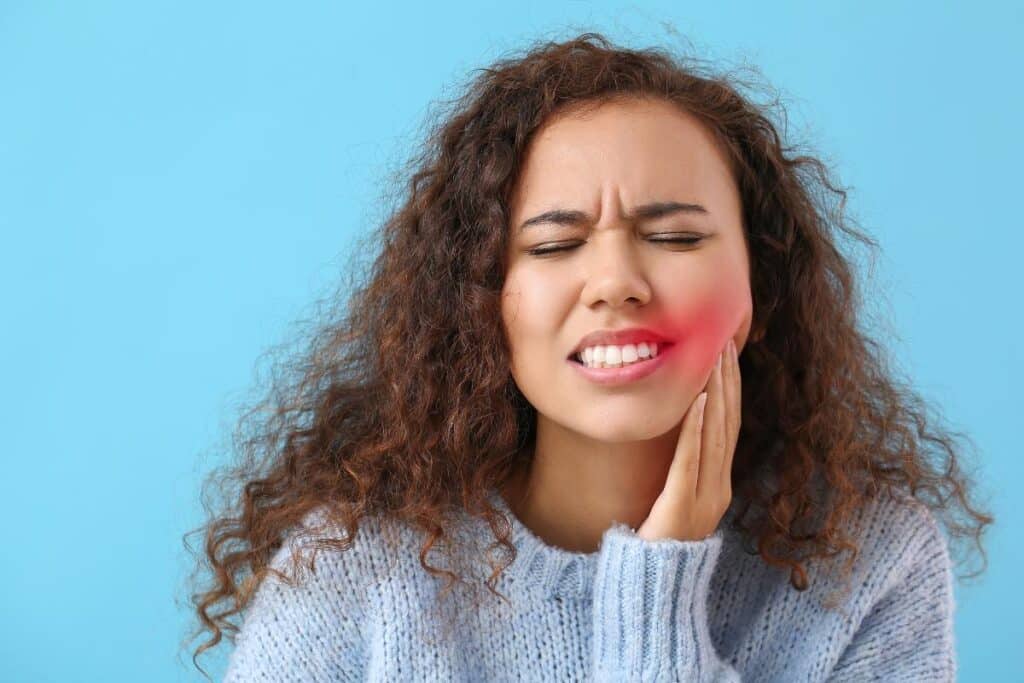
Tooth decay, commonly known as cavities, is one of the most prevalent oral health issues faced globally. If left untreated, it can progress to cause intense pain and further complications. Recognizing the root causes, practicing effective prevention methods, and seeking timely treatment can drastically reduce the chances of developing cavities and ensure a healthy smile. In this article we will discuss tooth decay, pain, causes, prevention and treaments.
What Causes Tooth Decay and Pain?
1. Bacteria and Plaque Formation:
The mouth is home to numerous bacteria, some of which feed on the sugars and starches found in the foods we consume. Thus, as these bacteria digest these substances, they produce acids. Over time, the bacteria, acids, food debris, and saliva combine to form a sticky substance called plaque that adheres to teeth. If plaque isn’t removed promptly, it can erode the enamel layer of teeth, leading to cavities.
2. Consuming Acidic or Sugary Foods and Drinks:
Frequent consumption of sugary or acidic foods and beverages can accelerate the process of enamel erosion. Examples include soft drinks, candies, pastries, and citrus fruits.
3. Poor Oral Hygiene:
Not brushing or flossing regularly allows plaque to accumulate and harden into tartar. Thus, tartar provides a protective shield for bacteria and can only be removed with professional cleaning.
4. Dry Mouth:
Saliva plays a crucial role in neutralizing acids produced by bacteria and washing away food particles. Also, conditions or medications causing reduced saliva flow can heighten the risk of cavities.
5. Tooth Grinding:
Consistent grinding of teeth can wear down the enamel, making teeth more susceptible to decay.
How to Prevent Tooth Decay and Pain?
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene:
Regularly brush your teeth with fluoride toothpaste at least twice a day. Also, ensure you also floss daily to remove food particles and plaque from between the teeth and under the gum line.
2. Limit Sugary and Acidic Intake:
Reduce the frequency of consuming sugary and acidic foods and drinks. When you do indulge, aim to brush your teeth soon after, or rinse your mouth with water.
3. Drink Tap Water:
Most tap water contains fluoride, which helps reduce tooth decay significantly. Also, fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, making it resistant to acid attacks.
4. Dental Sealants:
Consider getting dental sealants—a protective layer applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth, preventing plaque and acids from lodging into grooves.
5. Regular Dental Check-ups:
Visit your dentist at least twice a year for professional cleanings and check-ups. Also, they can detect early signs of decay and take corrective actions promptly.
How to Treat Tooth Decay and Pain?
1. Fluoride Treatments:
For early stages of decay, fluoride treatments can restore enamel, reversing a cavity in the making.
2. Fillings:
For established cavities, the decayed portion of the tooth is removed and filled with a suitable material such as amalgam, composite resins, or porcelain.
3. Crowns:
For severe decay where a significant portion of the tooth is damaged, a crown (or cap) is used to restore its shape, strength, and function.
4. Root Canals:
If tooth decay reaches the inner material of the tooth (pulp), a root canal may be necessary. The decayed pulp is removed, and the space is filled and sealed.
5. Tooth Extraction:
In extreme cases where the tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be the only option. The removed tooth can then be replaced with an implant, bridge, or denture.
Conclusion
Tooth decay is a progressive condition that can lead to significant pain and dental complications if not addressed promptly. Also, a combination of a balanced diet, stringent oral hygiene, and regular dental check-ups can keep decay at bay, ensuring that your smile remains bright and pain-free. Remember, proactive care is always better than reactive treatment; invest time in prevention to avoid potential pain and expenses in the future. If you or someone you know is looking to improve your health, share this article on Facebook or Twitter so that others can learn more about self-care.
Related Articles